Blockboard: The Perfect Balance of Stability and Affordability in Modern Woodworking
In This Post. All about Blockboard.
- Blockboard?
- Common Names.
- Manufacturing Process.
- Primary Applications.
- Advantages.
- Limitations.
- Recommendations
Blockboard
In the ever-evolving world of engineered wood products, Blockboard stands as a testament to innovative woodworking technology. This remarkable material, characterized by its unique construction of softwood strips sandwiched between plywood layers, offers an ingenious solution to many common woodworking challenges.
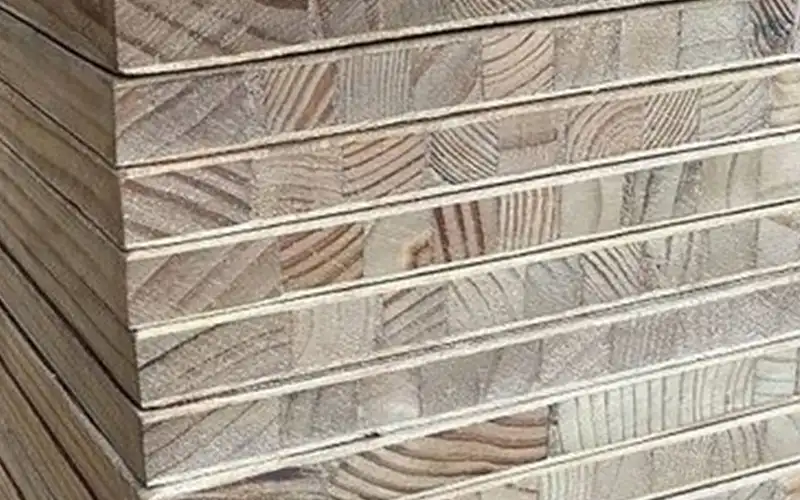

As we delve deeper into the world of Blockboard, we’ll discover how this versatile material has become an indispensable component in modern furniture making and interior design. Whether you’re a professional craftsperson or a homeowner planning your next renovation project, understanding Blockboard’s capabilities and characteristics is essential for making informed decisions about your woodworking projects.
Blockboard Common Trade Names and Grades
While Blockboard’s nomenclature is relatively straightforward, it’s known by various terms across different regions and markets:
- Blockboard: The standard and most widely recognized name
- Block Ply: A common alternative name in certain regions, emphasizing its relation to plywood
- Staved Core Board: Referring to its construction method
- Strip-Core Board: Describing its internal composition
- Softwood Composite Panel: Technical manufacturing description
- Engineered Wood Panel: Broader categorization
- Lightweight Wood Board: Performance-based description
- Structural Composite Board: Industrial classification
Blockboard Manufacturing Excellence
The creation of blockboard involves a sophisticated, multi-stage manufacturing process that transforms raw softwood materials into a high-performance engineered product. The journey begins with carefully selected softwood, typically pine or spruce, chosen for its consistent grain structure and lightweight characteristics.
Initial stages involve precise cutting of softwood strips, which are meticulously sorted and graded for uniformity. Each strip undergoes careful inspection to ensure minimal defects and consistent dimensions. The strips are then arranged edge-to-edge, creating a solid core that forms the board’s fundamental structure.
The core formation process requires exceptional precision. Strips are positioned to maximize structural integrity, with careful attention to grain orientation and potential stress points. Advanced adhesive technologies play a crucial role, with specialized wood glues ensuring strong, durable bonds between individual strips.
After core formation, the material enters a high-pressure lamination phase. Thin plywood sheets are applied to both sides of the core, creating a sandwich-like structure. Industrial presses apply controlled pressure and heat, activating the adhesive and creating a unified, stable panel. Temperature and pressure are carefully monitored to ensure optimal bonding without compromising wood fibers.
Final stages involve surface treatments, which may include sanding, veneer application, or protective coatings. Quality control inspections assess dimensional accuracy, structural integrity, and surface finish, ensuring each panel meets stringent industry standards.
Greenply Industries, Century Plyboards, Kitply Industries and Sarda Plywood Industries are the major Blockboard manufactures in india
Blockboard key Applications
Blockboard’s versatility extends across numerous sectors, making it a preferred material for diverse applications. In residential interiors, it serves as an excellent substrate for custom furniture, providing lightweight yet stable surfaces for bookshelves, tables, and wall paneling. Its uniform structure allows for clean, precise cuts and seamless finishes.
Commercial environments leverage blockboard’s properties in office furniture, partition systems, and modular design solutions. The material’s dimensional stability makes it ideal for creating large, flat surfaces that maintain their shape under varying environmental conditions. Architects and interior designers appreciate its ability to support complex design concepts while remaining economically viable.
Prefabricated housing and construction sectors increasingly adopt blockboard for non-load-bearing interior components. Its ease of manipulation, consistent performance, and cost-effectiveness position it as an attractive alternative to traditional building materials. From temporary structures to permanent installations, blockboard offers flexible solutions across different architectural contexts

Design Your Dream Interior: Explore Our Modular Interior Design Services
Launch Your Modular Interior Journey with Align Designs: Find the Best Plywood and Hardware Fittings in Our Curated List.
✔️Free 3D Designs
✔️Color selection
✔️45 Days Deliver
✔️15 years Guarantee
structural plywood Advantages
Blockboard’s advantages extend far beyond its basic structural properties, positioning it as a sophisticated solution in modern design and construction. Its lightweight nature represents a significant engineering achievement, allowing for easier transportation, reduced installation costs, and simplified handling compared to traditional solid wood panels
The material’s exceptional dimensional stability distinguishes it from competitors like particleboard or medium-density fiberboard (MDF). Unlike these alternatives, blockboard maintains its structural integrity under varying environmental conditions, resisting warping and deformation. This stability ensures long-term performance and aesthetic consistency in both furniture and architectural applications.
Manufacturing efficiency contributes to the material’s economic appeal. The production process requires minimal adhesive compared to other engineered wood products, reducing environmental impact and production costs. Moreover, the ability to use lower-grade softwoods in the core further enhances its cost-effectiveness without compromising overall performance.
Aesthetic versatility represents another compelling advantage. Blockboard’s uniform surface accepts various finishing techniques, including veneering, painting, and lamination. Designers can easily transform the material to match diverse stylistic requirements, from rustic to contemporary design schemes.
Understanding Limitations of structural plywood
Despite its numerous benefits, blockboard presents certain limitations that require careful consideration during specification and application. Its structural composition, while advantageous in many scenarios, results in lower overall strength compared to solid plywood or hardwood alternatives.
Manufacturing tolerances can introduce potential inconsistencies, particularly regarding core density and potential internal gaps. These variations may compromise the material’s performance in high-stress applications or environments requiring exceptional load-bearing capacity. Careful selection and quality control become crucial in mitigating these potential limitations.
Environmental sensitivity remains a consideration, with potential for moderate expansion or contraction under extreme humidity or temperature variations. While generally more stable than solid wood, blockboard still requires appropriate acclimatization and protective treatments in challenging environmental conditions.
Home Interior Recommendations
- Living Room Applications:
- Ideal for floating shelves
- Perfect for custom media units
- Excellent for modular furniture design
- Kitchen Implementations:
- Suitable for lightweight cabinetry
- Recommended for pantry shelving
- Excellent for decorative panel installations
- Bedroom Furniture:
- Ideal for headboard constructions
- Perfect for built-in wardrobes
- Suitable for drawer component manufacturing
- Home Office:
- Recommended for desk surfaces
- Excellent for modular storage solutions
- Ideal for partition wall systems
Professional Recommendations
Installation recommendations emphasize proper edge sealing and surface preparation. Applying appropriate edge treatments prevents moisture infiltration and enhances the material’s long-term durability. Utilizing compatible adhesives and fasteners designed for engineered wood ensures optimal performance and structural integrity.
Design professionals should consider blockboard’s inherent characteristics during specification. While versatile, the material requires thoughtful integration into overall design concepts. Leveraging its lightweight properties while understanding its load-bearing limitations allows for innovative and practical solutions.
Maintenance strategies include periodic inspection for potential moisture exposure or surface wear. Simple protective treatments can significantly extend the material’s useful life. Proper sealing and finishing techniques help mitigate environmental sensitivity and maintain aesthetic appeal.