HDF (High Density Fiberboard) The Complete Guide to : A Modern Interior Design Essential
In This Post. All about High Density Fiberboard.
- HDF?
- Common Names.
- Manufacturing Process.
- Primary Applications.
- Advantages.
- Limitations.
- Recommendations
High Density Fiberboard - HDF
High Density Fiberboard (HDF) stands as a testament to modern engineering in the world of wood products. This sophisticated engineered wood material has revolutionized interior design and construction practices since its inception.

Created through an intricate process of compressing wood fibers with advanced resins under extreme pressure and heat, HDF delivers exceptional density, strength, and moisture resistance. While many mistake it for standard plywood or MDF, HDF’s unique properties set it apart in both performance and versatility. The material’s evolution from a simple wood composite to a preferred choice in high-end interior applications showcases its remarkable journey in the construction industry.
HDF Common Trade Names and Grades
In the market, HDF goes by several names, each reflecting its properties or applications:
- High Density Fiberboard (HDF) – The most common and technically accurate name
- Hardboard – A term often used in North America, reflecting its superior hardness
- High Density Fiberboard Wood – A comprehensive term emphasizing its wood-based nature
- Compressed Wood Fiberboard – Highlighting the manufacturing process
- Super MDF – Sometimes used to distinguish it from standard MDF
- Ultra-dense Fiberboard – Used in some European markets
- Grade 7 Fiberboard – A technical classification based on density
HDF Manufacturing Excellence
The process begins in sustainable forests, where wood residuals and chips are carefully selected for their fiber quality. These materials undergo a sophisticated defibration process, where they’re broken down into individual wood fibers using steam and mechanical pressure. The resulting fibers are then dried to a precise moisture content, typically between 8-10%, to ensure optimal bonding.
The heart of HDF production lies in its unique fiber treatment. The wood fibers are mixed with specially formulated thermosetting resins, typically melamine-urea-formaldehyde or phenol-formaldehyde, along with performance-enhancing additives like wax emulsions for moisture resistance.
This mixture undergoes a carefully controlled pressing process where temperatures exceed 200°C (392°F) and pressures reach up to 800-1000 psi. This extreme environment causes the resins to cure and the fibers to compress and bond, creating the characteristic high-density structure of HDF.
The final stages involve precise temperature and humidity control during cooling, which prevents internal stresses and ensures dimensional stability. The resulting panels undergo rigorous quality control measures, including density profile analysis and surface quality inspections, before being cut to standard sizes.
Greenply Industries, Century Plyboards, Kitply Industries and Sarda Plywood Industries are the major HDF manufactures in india
HDF key Applications
In residential settings, HDF has become the backbone of modern flooring solutions. The material’s exceptional density and structural stability make it the preferred substrate for laminate flooring, providing the necessary impact resistance and dimensional stability that ensures long-lasting performance even in high-traffic areas.
In furniture manufacturing, HDF has revolutionized the production of contemporary pieces. Its smooth surface and excellent machinability allow for intricate designs and precise joinery. Cabinet makers particularly value HDF for its ability to hold hardware securely and its compatibility with various finishes. The material’s consistency and lack of natural defects make it ideal for painted furniture, where a flawless surface is essential.
The commercial sector has embraced HDF for its exceptional performance in retail fixtures and office furniture. Its ability to withstand daily wear while maintaining its appearance has made it a go-to material for display units, workstations, and architectural elements. In educational and healthcare facilities, HDF’s moisture resistance and easy-to-clean surface have made it a practical choice for built-in furniture and wall panels.
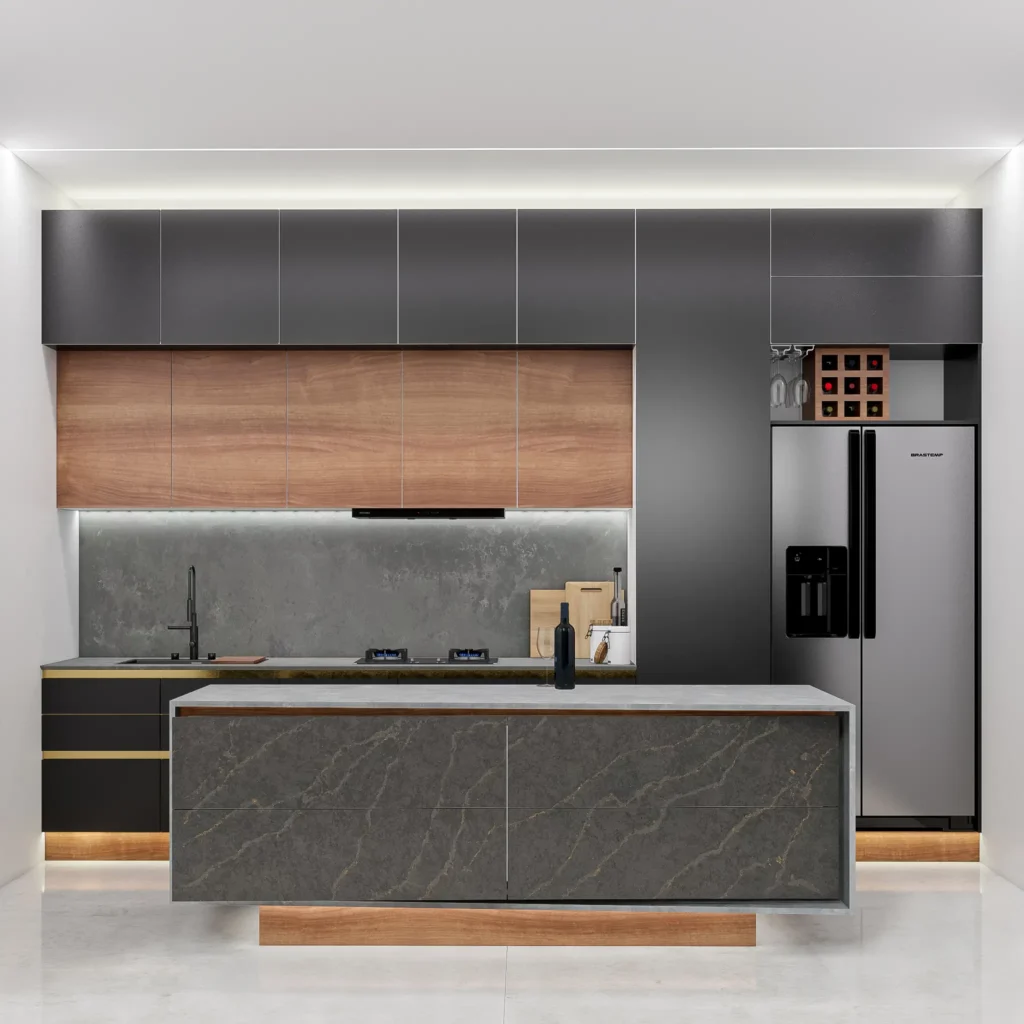

Design Your Dream Interior: Explore Our Modular Interior Design Services
Launch Your Modular Interior Journey with Align Designs: Find the Best Plywood and Hardware Fittings in Our Curated List.
✔️Free 3D Designs
✔️Color selection
✔️45 Days Deliver
✔️15 years Guarantee
HDF Advantages
The superior characteristics of HDF have established it as a premier choice in modern construction and design. Its exceptional density, typically ranging from 800-1040 kg/m³, creates a material that outperforms traditional wood products in many aspects.
This high density translates to remarkable screw-holding capacity and superior edge detail, making it ideal for furniture assembly and architectural applications requiring precise finishing.
Moisture resistance in Ultra-dense Fiberboard represents a significant advancement over traditional fiberboards. The manufacturing process incorporates specialized water-repelling agents throughout the material, not just on the surface.
This integral protection means that even if the surface is breached, the internal structure maintains its integrity better than conventional wood products. While not completely waterproof, this characteristic makes HDF particularly suitable for bathrooms, kitchens, and other areas with varying humidity levels.
The material’s dimensional stability is another crucial advantage. Unlike natural wood, which can expand and contract significantly with environmental changes, Hardboard maintains its dimensions within much tighter tolerances. This stability is particularly valuable in large installations where minimal movement is essential for maintaining the integrity of the overall design.
Understanding Limitations of HDF
The material’s relationship with moisture requires careful consideration. Though more resistant than many alternatives, prolonged exposure to water can still cause dimensional changes and potential degradation.
The manufacturing process that gives HDF its strength also creates certain structural limitations. The high-density structure, while excellent for many applications, means the material doesn’t have the same kind of internal flexibility found in traditional plywood.
This can make it less suitable for applications requiring significant bending or flexing. Additionally, the material’s weight, while beneficial for stability, can present challenges in transportation and installation.
Cost considerations also play a role in project planning. While HDF’s durability often provides excellent long-term value, its initial cost may be higher than some alternatives. This price difference reflects the more complex manufacturing process and higher quality standards required for Hardboard production.
Home Interior Recommendations
For optimal utilization of HDF in home interiors, consider these design-focused applications:
Flooring Solutions
- Use as a base for premium laminate flooring in high-traffic areas
- Consider HDF-core engineered wood flooring for a more natural look
- Ideal for open-plan living spaces where consistent flooring is crucial
Wall Treatments
- Perfect for decorative wall panels and wainscoting
- Excellent substrate for wallpaper application
- Ideal for creating feature walls with textured finishes
Custom Cabinetry
- Superior choice for kitchen cabinet doors and drawer fronts
- Excellent for built-in wardrobes and storage solutions
- Perfect for bathroom vanities and storage units
Furniture Applications
- Ideal for contemporary furniture pieces requiring smooth, painted finishes
- Perfect for children’s furniture due to its durability
- Excellent for built-in office furniture and study areas
Professional Recommendations
High Density Fiberboard panels should be stored horizontally in a controlled environment for at least 48 hours before installation to ensure dimensional stability. This acclimatization period is crucial for preventing future warping or movement.
When it comes to finishing, HDF’s dense, smooth surface accepts a wide range of treatments, but proper preparation is essential. Light sanding between coats of finish and the use of high-quality primers designed for engineered wood products will ensure optimal results. For painted applications, water-based acrylic paints typically provide the best combination of adhesion and durability.
In terms of joinery and assembly, HDF responds well to traditional woodworking techniques but requires specific considerations. Pre-drilling is essential for screw fixings, and the use of appropriate adhesives designed for engineered wood products will ensure long-lasting joints. Edge treatments deserve particular attention – while HDF edges can be finished similarly to natural wood, sealing them is crucial for moisture resistance.
it’s recommended to source High Density Fiberboard products certified by recognized environmental organizations. Many manufacturers now offer HDF with reduced formaldehyde emissions and recycled content, contributing to healthier indoor environments and reduced environmental impact.
In conclusion, HDF represents a significant advancement in engineered wood products, offering a versatile and reliable material for modern interior design applications. Its combination of strength, stability, and finishing capabilities makes it an excellent choice for a wide range of projects, from residential renovations to commercial installations.